Fire extinguishers are very important tools for controlling small fires and preventing them from spreading. However, knowing how to use a fire extinguisher properly ways is as important as having one readily available. In this article, we will explore the proper use of fire extinguishers with essential information on how to extinguish a fire using these life-saving devices effectively.
In India, about 25,000 plus fires happen every year and cause a lot of damage and loss of life. Knowing how to use a fire extinguisher can save your home and family.
Key Takeaways
- Fire extinguishers play a very important role in fire safety equipment for every home and workplace.
- Knowing the basic components and types of fire extinguishers is very important for proper usage.
- The PASS technique (Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep) is important for effectively operating a fire extinguisher.
- Proper storage, maintenance, and inspection of fire extinguishers are very important for ensuring emergency response.
- Fire safety knowledge with regular practice drills can help your family respond quickly and confidently in a fire emergencies
Understanding Fire Extinguisher
When we use a fire extinguisher, first you need to know its components and what fire types it can fight. A fire extinguisher is a very useful tool for small fires. It controls fires from getting more. Let’s look at this important safety tool.
Some Components of a Fire Extinguisher
A standard fire extinguisher has some components which are:
- Cylinder: It is a strong, pressurized container that has a fire-fighting agent.
- Nozzle: It is the part where the fire-fighting agent comes out.
- Handle: It is used to release the agent by squeezing or pressing.
Different Types of Fires
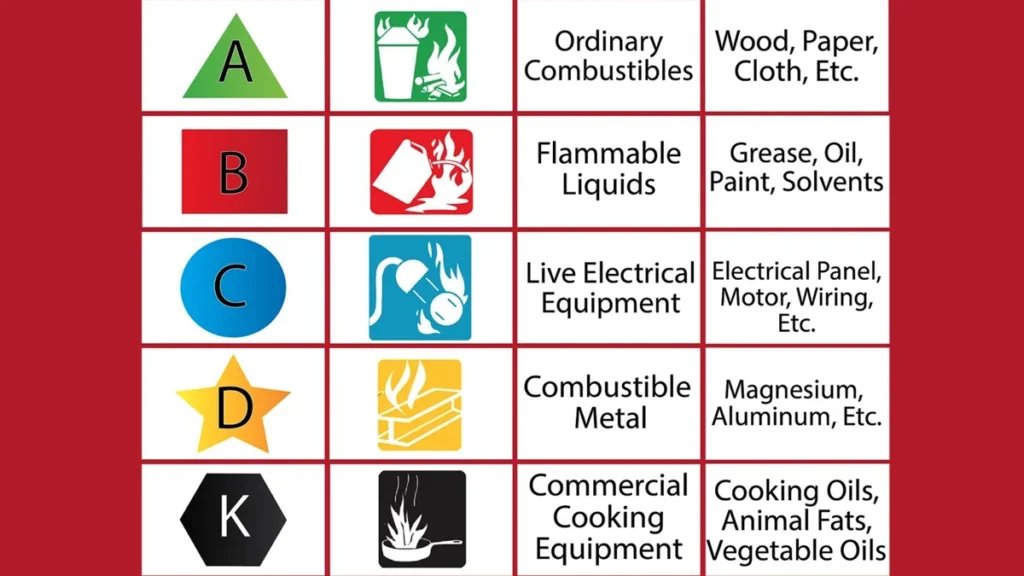
Different types of fire are:
- Class A: Materials like wood, paper, and cloth.
- Class B: Flammable liquids and gases, like gasoline and propane.
- Class C: Electrical equipment, like appliances and electronics.
- Class D: Combustible metals, like magnesium and sodium.
- Class K: Cooking oils and fats, found in commercial kitchens.
Safety Pin and Pressure Gauge
The safety pin and pressure gauge are also important components of a fire extinguisher the safety pin controls the handle from being pressed by mistake, the pressure gauge shows if the extinguisher is ready to use in fire emergencies.
The components and fire types of a fire extinguisher are very important for safety and this tool helps in safely in a fire.
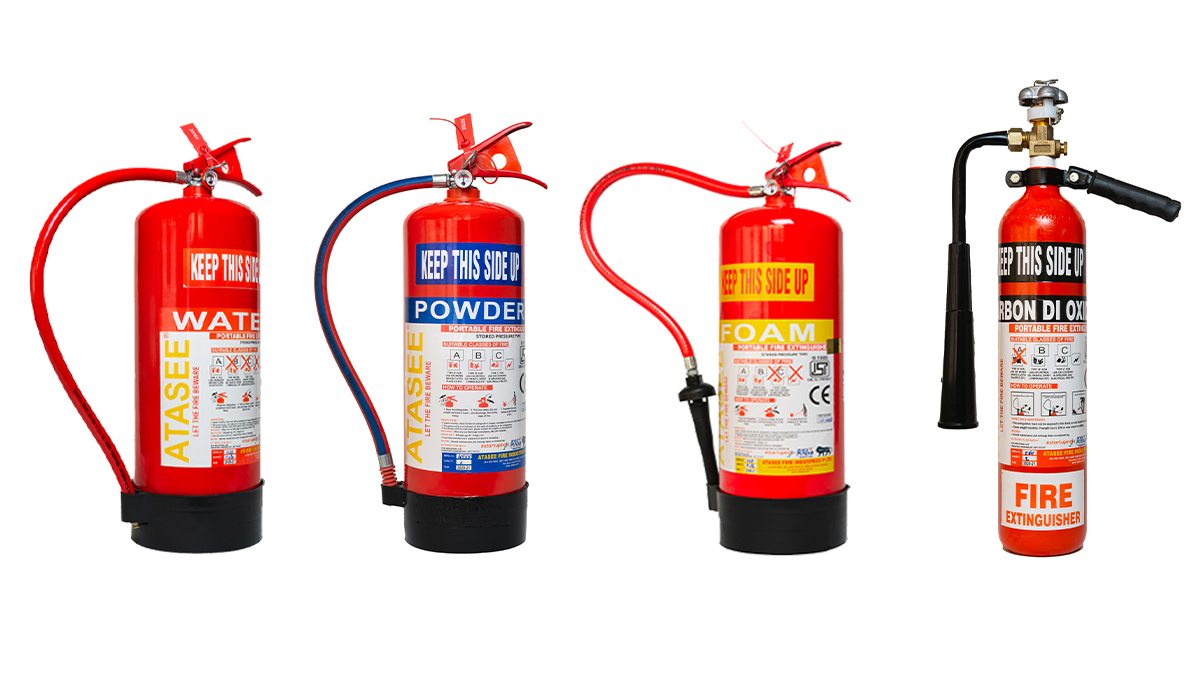
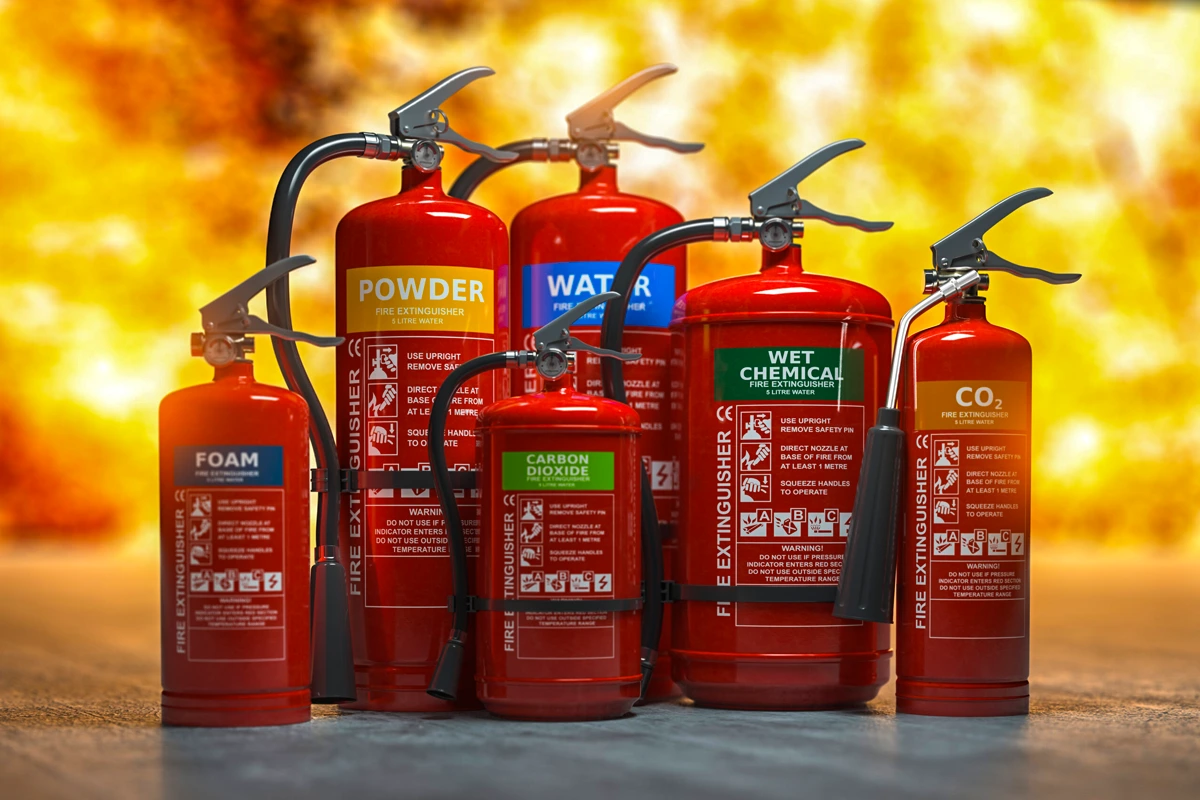
Types of Fire Extinguishers In India

There are many types of Fire Extinguishers to choose from, each is made for different types of fires. Let’s look at what fire extinguishers are perfect for which types of fires.
Water-Based Extinguishers
Water-based extinguishers are very common and reasonable and it used for Class A fires, like wood, paper, and cloth. They cool the fire and stop it from spreading.
Foam Extinguishers
Foam fire extinguishers are perfect for Class B fires, which include flammable liquids and gases. The foam covers the fire and controls it from spreading. These are best for kitchens and garages.
Dry Powder Extinguishers
Dry powder extinguishers can fight fires like Class A, B, and C fires and control the fire’s chemical reaction. These are best for homes and offices and work on many types of fires.
CO2 Extinguishers
CO2 extinguishers are best for Class B and C fires which take away oxygen, which stops the fire. These are perfect for electrical equipment and don’t leave a residue.
| Extinguisher Type | Suitable for | Advantages | Limitations |
| Water-based | Class A fires | Affordable, effective on ordinary combustibles | Not suitable for electrical or flammable liquid fires |
| Foam | Class B fires | Effective on flammable liquids and gases | Not suitable for electrical fires |
Dry Powder | Class A, B, and C fires | Versatile, effective on many types of fires | May leave a mess after use |
| CO2 | Class B and C fires | Safe for electrical equipment, leaves no residue | Less effective on deep-seated fires |
Choosing the right fire extinguisher plays a very important role. And you can select it with a fire safety expert who can help you pick the best one.
How to Use Fire Extinguisher: PASS Method
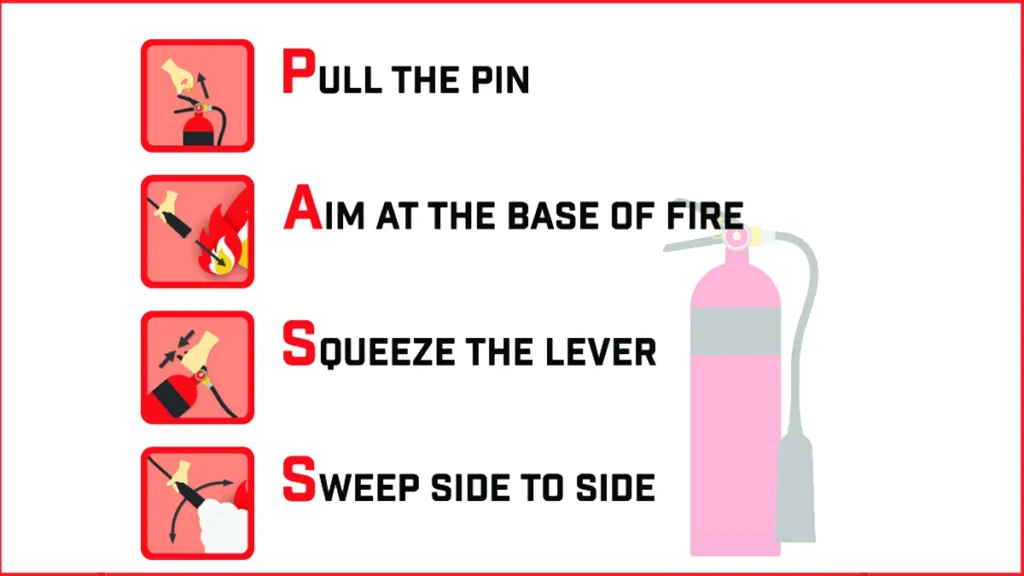
Understanding how to use a fire extinguisher properly is paramount in a fire emergency. One of the most important techniques is the PASS method, which a fire extinguisher supplier describes with some simple steps which are.
P – Pull the Pin
In the first step, the PASS method is to pull the pin at the top of the fire extinguisher. This pin works as a safety technique, to control accidental discharge. Hold the pin firmly and pull it straight out to remove it. By doing this, the tamper seal will be broken, enabling you to move on to the next phase.
A – Aim at the Base
After removing the pin, the fire extinguisher’s hose or nozzle has to be aimed. Instead of hitting the flames directly, aim the extinguisher toward the fire’s base. To effectively extinguish the fire, you must cut off its fuel supply, which is accomplished by focusing on the base. Keep in mind to keep a safe distance while trying to stay clear of any possible dangers.
S – Squeeze the Handle
The extinguisher should now be pointed at the fire’s base, and the handle should be squeezed. The handle releases the extinguishing agent and acts as the activation mechanism. Give the handle constant pressure to ensure that the extinguishing agent flows properly. You may start the discharge and allow the extinguishing chemical to efficiently put out the fire by squeezing the handle.
S – Sweep side-to-side
Sweeping the hose or nozzle from side to side is important when the extinguishing material is released. This sweeping action ensures complete suppression by sweeping the whole fire area. Repeat the sweeping motion until the fire is put out or the extinguisher is completely empty. Keep in mind to keep a safe distance from the fire and to be alert for any possible re-ignition.
Tips for Using the PASS Method Effectively
- Size Matters: Fire extinguishers come in different sizes with varying capacities and discharge times. Learn about the specific extinguisher you have to ensure it has enough agent to put out a fire.
- Know Your Fire Extinguisher: Understand the type of extinguisher you have and the fire class it is suitable for (e.g., Class A for ordinary combustibles, Class B for flammable liquids, Class C for electrical fires, or Class K for cooking oil). Using the wrong one can be ineffective and dangerous.
- Communicate and Evacuate: Prioritise safety. If the fire spreads quickly, smoke fills the area, or you’re unsure about using the extinguisher, evacuate immediately and call emergency services. Follow evacuation plans and warn others.
- Stay Prepared: Regularly practice the PASS method and learn about fire extinguishers to build confidence and be ready for emergencies.
Safety first!
How to Use a Fire Extinguisher?
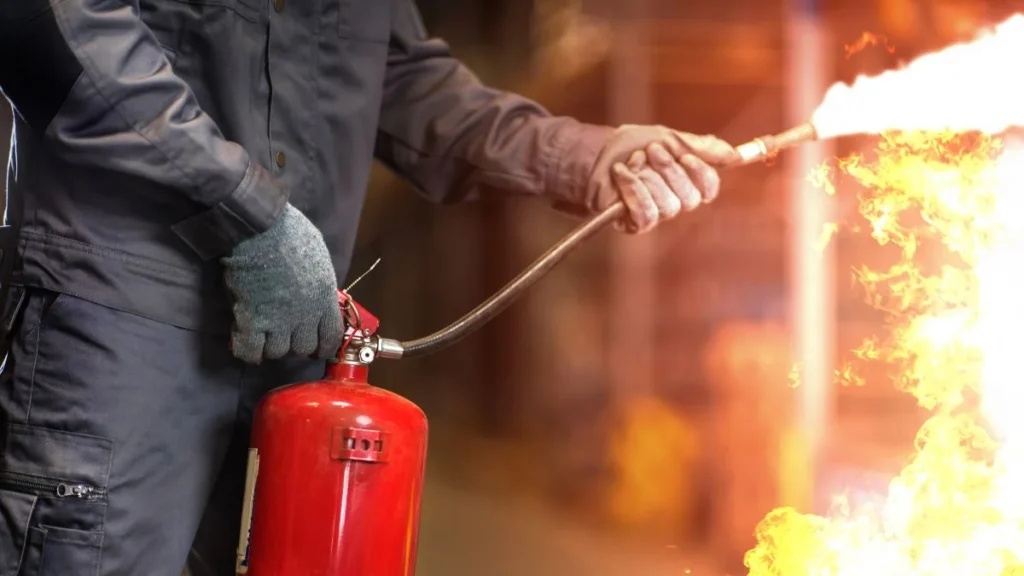

Using a fire extinguisher right now can save your family members at home, or employees at the workplace in a fire emergency. Here’s a simple guide on how to use it correctly:
- Determine the situation: Confirm that there is not much of a fire and that you can leave without incident. Get out and contact the fire department if it’s too large.
- Pull out the pin: Find the extinguisher’s pin and firmly pull it to open it.
- Aim at the Base: Direct the nozzle toward the base of the fire instead of the flames. This helps in putting out the fire and stopping it from spreading.
- Squeeze the Handle: The firefighting agent is released by carefully pressing the handle.
- Sweep Side to Side: While maintaining your aim at the base, move the nozzle side to side. This covers all of the fire areas.
Effective use of a fire extinguisher needs prompt and appropriate action. Practicing and receiving training can help you get ready for a fire.
| Common Errors to Stay Away | Best Techniques for Effective Use |
| The extinguisher should be pointed at the flames rather than the fire’s base. Using the extinguishing agent randomly or too quickly when utilizing the extinguisher, keep your back to the flames. Fighting a fire that has already gotten out of control a steady, balanced position when applying the extinguisher. | The extinguishing agent should be applied gradually and carefully. The extinguisher nozzle and your body should remain aimed at the fire’s foundation. Make sure the fire is small and controlled and that you have a clear escape path. |
You can better handle fire and ensure the safety of everyone and everything by paying attention and using the suggestions below.
Maintenance and Inspection Schedule
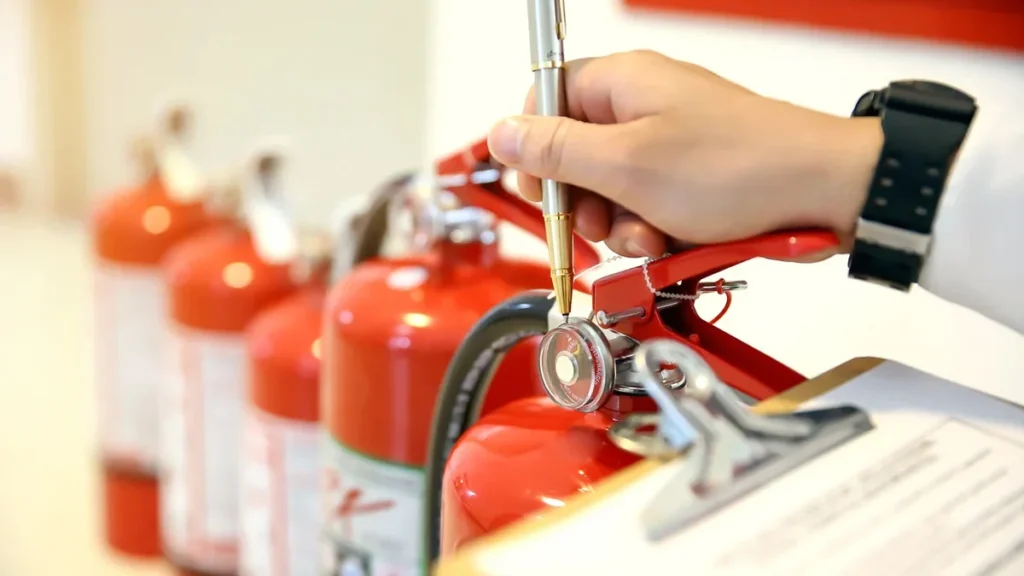

Regular maintenance and inspection schedules are very important to keeping your fire extinguisher ready. We must stay proactive to prevent our family members and homes from fires as homeowners.
Fire Extinguisher Maintenance Tips
- Monthly Checks:
- Check for damage or tampering.
- Check the pressure gauge to ensure it’s properly pressurized.
- Confirm the safety pin is in place and the handle is clear.
- Annual Servicing:
- Schedule professional servicing yearly.
- Clean and maintain all parts.
- Recharge the extinguisher’s agent and gas.
- Replace worn or damaged parts.
- Ensure it meets safety and performance standards.
By following this maintenance plan, you can trust your fire extinguisher to work when needed.
“To make sure your fire extinguisher works in an emergency, regular maintenance is essential.”
Bottom Line:
Fire extinguishers are very important tools for controlling small fires and preventing them from spreading. However, knowing how to use a fire extinguisher properly ways is as important as having one readily available. Choosing the right fire extinguisher plays a very important role. And you can select it with a fire safety expert who can help you pick the best one.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to use a fire extinguisher?
Pull the pin to unlock the extinguisher and next Aim at the base (bottom) of the fire with a stand 6- 10 feet away, now squeeze the lever to discharge the agent, and last sweep the spray from left to right until the fires are extinguished.
What are the steps used for a fire extinguisher?
1. Dial 911. …
2. Pull the Pin. …
3. Aim. …
4. Squeeze. …
5. Sweep Side to Side, left to Right
6. Extinguish the Fire. …
What is the basic rule to use the fire extinguisher?
Fire extinguishers make it easy to remember how to use a fire extinguisher by using the PASS method, which means Pull, Aim, Squeeze, and Sweep.
What are the important fire extinguisher components?
A fire extinguisher’s components are a cylinder, nozzle, and handle. In these components, the cylinder has the extinguishing agent, the nozzle directs the agent at the fire and the handle is used to activate it.
What are the different types of fires?
There are five main types of fire A type of fire involves ordinary combustibles, B types of fire are related to flammable liquids and gases, C types of fire involve energized electrical equipment, D types of fire are for combustible metals, and K types of fire are for cooking oils and fats.
What is the role of the safety pin and pressure gauge in a fire extinguisher?
The safety pin helps to stop the extinguisher from accidentally going off and the pressure gauge helps if the extinguisher is ready to use.
What are the different types of fire extinguishers available in India?
The different types of fire extinguishers are water, foam, dry powder, and CO2 extinguishers in India. Each type of fire extinguisher is made for different types of fires.




